UNCOVERING
THE PIGMENTS
AND TECHNIQUES
USED TO PAINT
THE BERLIN WALL
Street art takes many forms, and the vibrant murals
on the Berlin Wall—both before and after its fall—
capture expressions of public opinion. However, the
secrecy surrounding their creation often complicates
efforts to preserve them. Now, researchers reporting
in the Journal of the American Chemical Society have
analyzed paint chips from this historic site using a
combination of a handheld detector and artificial
intelligence (AI) data analysis to uncover valuable
information.
“This research highlights the powerful synergy
between chemistry and deep learning in quanti-
fying materials, as demonstrated by the pigments
that make street art so captivating,” said Francesco
Armetta, a co-author of the study.
Restoration and conservation efforts depend on
understanding the materials and techniques used
in artwork. However, Berlin Wall painters didn’t
document their processes. In past studies of other
historic artifacts, scientists used nondestructive
techniques like Raman spectroscopy to identify
pigments in fragments brought to the lab. While
portable Raman devices allow for on-site analysis,
they lack the precision of full-sized lab equipment. To
address this, Armetta, Rosina Celeste Ponterio, and
colleagues wanted to develop an AI algorithm that
could analyze the output of portable Raman devices
to more accurately identify pigments and dyes. In
an initial test of the new approach, they analyzed 15
paint chips from the Berlin Wall.
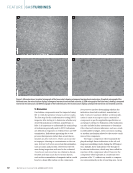
Magnified images revealed that the chips
contained two or three layers of paint, with visible
brushstrokes. A white base coat, likely used to
prepare the wall, was present in the layer closest to
the masonry. Using a handheld Raman spectrom-
eter, the researchers compared the paint chips’
spectra to a commercial pigment library. They
identified the primary pigments in the samples as
azopigments (yellow and red chips), phthalocyanins
(blue and green chips), lead chromate (green chips),
and titanium white (white chips). These results were
confirmed with additional nondestructive tech-
niques, including X-ray fluorescence and optical fiber
reflectance spectroscopy.
Then, the researchers mixed pigments from a
commercial acrylic paint brand (used in Germany
since the 1800s) with titanium white in varying ratios,
trying to match colors and the range of tints typical
for painters. A knowledge of these ratios could
help art conservators prepare the right materials for
restoration, the researchers explained. They trained
a machine-learning algorithm with the Raman spec-
tral data from these mixtures to determine pigment
percentages. The approach indicated that the Berlin
Wall paint chips contained up to 75% pigment,
depending on the color tone, and varying levels of
titanium white.
The researchers suggested their AI-enhanced
approach could provide high-quality information for
art conservation, forensics, and materials science,
especially in situations where transporting lab equip-
ment to a site is impractical.
The study was supported by the Project Eurostart
“Punic or Greek weapons? The answer in the invis-
ible” and EEPP Italian Ministry of Universities and
Research Funds.
The paper’s abstract and supporting information
are available at http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/
jacs.4c12611.
SCANNER
Micrographs of the surface and
cross-sections of representative
fragments from the Berlin Wall,
which was the subject of a recent
study aiming to develop an AI
algorithm to more accurately
analyze data and identify the
pigment and dyes originally
used to paint the wall.
8
M A T E R I A L S E V A L U A T I O N • F E B R U A R Y 2 0 2 5
2502 ME Feb.indd 8 1/23/25 1:21 PM
CREDIT:
JOURNAL
OF
THE
AMERICAN
CHEMICAL
SOCIETY
THE PIGMENTS
AND TECHNIQUES
USED TO PAINT
THE BERLIN WALL
Street art takes many forms, and the vibrant murals
on the Berlin Wall—both before and after its fall—
capture expressions of public opinion. However, the
secrecy surrounding their creation often complicates
efforts to preserve them. Now, researchers reporting
in the Journal of the American Chemical Society have
analyzed paint chips from this historic site using a
combination of a handheld detector and artificial
intelligence (AI) data analysis to uncover valuable
information.
“This research highlights the powerful synergy
between chemistry and deep learning in quanti-
fying materials, as demonstrated by the pigments
that make street art so captivating,” said Francesco
Armetta, a co-author of the study.
Restoration and conservation efforts depend on
understanding the materials and techniques used
in artwork. However, Berlin Wall painters didn’t
document their processes. In past studies of other
historic artifacts, scientists used nondestructive
techniques like Raman spectroscopy to identify
pigments in fragments brought to the lab. While
portable Raman devices allow for on-site analysis,
they lack the precision of full-sized lab equipment. To
address this, Armetta, Rosina Celeste Ponterio, and
colleagues wanted to develop an AI algorithm that
could analyze the output of portable Raman devices
to more accurately identify pigments and dyes. In
an initial test of the new approach, they analyzed 15
paint chips from the Berlin Wall.
Magnified images revealed that the chips
contained two or three layers of paint, with visible
brushstrokes. A white base coat, likely used to
prepare the wall, was present in the layer closest to
the masonry. Using a handheld Raman spectrom-
eter, the researchers compared the paint chips’
spectra to a commercial pigment library. They
identified the primary pigments in the samples as
azopigments (yellow and red chips), phthalocyanins
(blue and green chips), lead chromate (green chips),
and titanium white (white chips). These results were
confirmed with additional nondestructive tech-
niques, including X-ray fluorescence and optical fiber
reflectance spectroscopy.
Then, the researchers mixed pigments from a
commercial acrylic paint brand (used in Germany
since the 1800s) with titanium white in varying ratios,
trying to match colors and the range of tints typical
for painters. A knowledge of these ratios could
help art conservators prepare the right materials for
restoration, the researchers explained. They trained
a machine-learning algorithm with the Raman spec-
tral data from these mixtures to determine pigment
percentages. The approach indicated that the Berlin
Wall paint chips contained up to 75% pigment,
depending on the color tone, and varying levels of
titanium white.
The researchers suggested their AI-enhanced
approach could provide high-quality information for
art conservation, forensics, and materials science,
especially in situations where transporting lab equip-
ment to a site is impractical.
The study was supported by the Project Eurostart
“Punic or Greek weapons? The answer in the invis-
ible” and EEPP Italian Ministry of Universities and
Research Funds.
The paper’s abstract and supporting information
are available at http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/
jacs.4c12611.
SCANNER
Micrographs of the surface and
cross-sections of representative
fragments from the Berlin Wall,
which was the subject of a recent
study aiming to develop an AI
algorithm to more accurately
analyze data and identify the
pigment and dyes originally
used to paint the wall.
8
M A T E R I A L S E V A L U A T I O N • F E B R U A R Y 2 0 2 5
2502 ME Feb.indd 8 1/23/25 1:21 PM
CREDIT:
JOURNAL
OF
THE
AMERICAN
CHEMICAL
SOCIETY