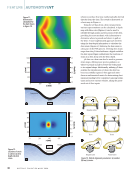
be addressed to fully realize their poten-
tial. VR, AR, and MR technologies are
advancing rapidly, with current hardware
limitations—such as resolution, field of view,
and battery life—being improved with
each new iteration. Integrating immersive
tools and digital twins with existing inspec-
tion workflows and data management
systems is paving the way for faster adop-
tions of digital inspection capabilities. This
integration directly enhances operational
efficiency and boosts business return on
investment (ROI). Furthermore, the cost of
VR, AR, and MR technology is decreasing
rapidly as the technology matures and
more device options become available.
Finally, cloud computing and 5G networks
are making these technologies more
accessible, even in remote areas, which is
crucial for accelerating business adoption.
Adopting new technologies involves
a learning curve and requires effective
change management. As inspectors
and users become more familiar with
immersive technologies and digital
twins, adoption will accelerate, neces-
sitating changes at various levels within
the industry. The inspection industry
operates within a framework of strict
regulations, and aligning new technol-
ogies with these standards is essential.
Regulatory bodies are beginning to
recognize the advantages of VR, AR,
and MR technologies and are working
toward developing guidelines and
standards to facilitate their use. As the
benefits of these technologies become
more evident, regulatory acceptance
and standardization will inevitably be
addressed.
Concluding Remarks
Digital twins created from inspection
data can be utilized repeatedly across
multiple applications. When combined
with immersive 3D visualization, they offer
significant opportunities to transform the
inspection industry. Continuous advance-
ments in technology, improved business
integration, cost reduction, regulatory
acceptance, and innovations in AI will inev-
itably drive faster adoption in the inspec-
tion industry. As key barriers to entry are
eliminated, digital twins combined with
VR, AR, and MR are poised to become
integral tools in ensuring higher safety,
quality, and efficiency of inspections
across various sectors.
AUTHOR
Ali Merchant, PhD: Founder and CEO, iQ3
Connect, Woburn, MA ali@iq3connect.com
DISCUSSING
DIGITALIZATION
AND HOW IT’S
CHANGING NDT
The evolving role of digitalization and
advanced technologies in the nondestruc-
tive testing (NDT) industry was the focus
of the ASNT 2023 Annual Conference and
the main topic of a discussion INSPENET
TV had with ASNT CEO Neal Couture,
CAE, which is now available online. In the
interview, recorded during the final night
of the ASNT event last fall, Couture talks
about digitalization as it pertains to NDT
and shares how ASNT has managed to
unite the community of NDT experts,
highlighting the organization’s efforts
and achievements in creating a space
for discussing technical and business
challenges in the sector. Watch the full
interview at https://inspenet.com/video-tv/
industry-non-destructive-testing/.
INSPENET.COM
FREE DOWNLOAD
OF ULTRASONIC
TESTING UT
TRAINING BOOK
A revision of the practical exercise book
and field guide UT of Thin-Walled Steel
Pipe Flaws by Jimmy Ellis is now available
as a free PDF book download. The book
covers manual detection, characterizing,
and sizing of thin-walled steel pipe flaws,
with links to 57 YouTube videos. The
previous edition has been downloaded
over 2600 times in the past five years. The
latest version is expanded to be appli-
cable to more industry segments. The
book and its accompanying videos are
appropriate for beginners just starting
to learn how to do manual UT but
progresses to many advanced techniques
the experienced UT technician could find
useful. Navigation is enhanced for the
experienced user, with detailed contents
and subject tables.
UTOFPIPELINEDIGS.COM
NEUTRON IMAGING
TECHNOLOGY
CONVENTIONAL
RADIOGRAPHY
A new anal-
ysis from
Phoenix
Neutron
Imaging
comparing
neutron
radiology to
more commonly used NDT techniques is
now available for free online. The 2024
Non-Destructive Testing Industry
Report first examines the current state of
the NDT market and the trends driving
NDT adoption before delving into head-
to-head comparisons of neutron imaging
with other NDT techniques, including
photos. “While neutron imaging is most
commonly practiced within the aero-
space and defense industries,” the report
states, “other markets are incorporating
it into their processes to improve quality,
safety, and accuracy in a variety of appli-
cations.” The report may be downloaded
at https://go.phoenixneutronimaging.
com/industry-report.
PHOENIXNEUTRONIMAGING.COM
NEWMEDIA
|
SCANNER
NDE OUTLOOK FROM P. 14
J U L Y 2 0 2 4 • M A T E R I A L S E V A L U A T I O N 15
tial. VR, AR, and MR technologies are
advancing rapidly, with current hardware
limitations—such as resolution, field of view,
and battery life—being improved with
each new iteration. Integrating immersive
tools and digital twins with existing inspec-
tion workflows and data management
systems is paving the way for faster adop-
tions of digital inspection capabilities. This
integration directly enhances operational
efficiency and boosts business return on
investment (ROI). Furthermore, the cost of
VR, AR, and MR technology is decreasing
rapidly as the technology matures and
more device options become available.
Finally, cloud computing and 5G networks
are making these technologies more
accessible, even in remote areas, which is
crucial for accelerating business adoption.
Adopting new technologies involves
a learning curve and requires effective
change management. As inspectors
and users become more familiar with
immersive technologies and digital
twins, adoption will accelerate, neces-
sitating changes at various levels within
the industry. The inspection industry
operates within a framework of strict
regulations, and aligning new technol-
ogies with these standards is essential.
Regulatory bodies are beginning to
recognize the advantages of VR, AR,
and MR technologies and are working
toward developing guidelines and
standards to facilitate their use. As the
benefits of these technologies become
more evident, regulatory acceptance
and standardization will inevitably be
addressed.
Concluding Remarks
Digital twins created from inspection
data can be utilized repeatedly across
multiple applications. When combined
with immersive 3D visualization, they offer
significant opportunities to transform the
inspection industry. Continuous advance-
ments in technology, improved business
integration, cost reduction, regulatory
acceptance, and innovations in AI will inev-
itably drive faster adoption in the inspec-
tion industry. As key barriers to entry are
eliminated, digital twins combined with
VR, AR, and MR are poised to become
integral tools in ensuring higher safety,
quality, and efficiency of inspections
across various sectors.
AUTHOR
Ali Merchant, PhD: Founder and CEO, iQ3
Connect, Woburn, MA ali@iq3connect.com
DISCUSSING
DIGITALIZATION
AND HOW IT’S
CHANGING NDT
The evolving role of digitalization and
advanced technologies in the nondestruc-
tive testing (NDT) industry was the focus
of the ASNT 2023 Annual Conference and
the main topic of a discussion INSPENET
TV had with ASNT CEO Neal Couture,
CAE, which is now available online. In the
interview, recorded during the final night
of the ASNT event last fall, Couture talks
about digitalization as it pertains to NDT
and shares how ASNT has managed to
unite the community of NDT experts,
highlighting the organization’s efforts
and achievements in creating a space
for discussing technical and business
challenges in the sector. Watch the full
interview at https://inspenet.com/video-tv/
industry-non-destructive-testing/.
INSPENET.COM
FREE DOWNLOAD
OF ULTRASONIC
TESTING UT
TRAINING BOOK
A revision of the practical exercise book
and field guide UT of Thin-Walled Steel
Pipe Flaws by Jimmy Ellis is now available
as a free PDF book download. The book
covers manual detection, characterizing,
and sizing of thin-walled steel pipe flaws,
with links to 57 YouTube videos. The
previous edition has been downloaded
over 2600 times in the past five years. The
latest version is expanded to be appli-
cable to more industry segments. The
book and its accompanying videos are
appropriate for beginners just starting
to learn how to do manual UT but
progresses to many advanced techniques
the experienced UT technician could find
useful. Navigation is enhanced for the
experienced user, with detailed contents
and subject tables.
UTOFPIPELINEDIGS.COM
NEUTRON IMAGING
TECHNOLOGY
CONVENTIONAL
RADIOGRAPHY
A new anal-
ysis from
Phoenix
Neutron
Imaging
comparing
neutron
radiology to
more commonly used NDT techniques is
now available for free online. The 2024
Non-Destructive Testing Industry
Report first examines the current state of
the NDT market and the trends driving
NDT adoption before delving into head-
to-head comparisons of neutron imaging
with other NDT techniques, including
photos. “While neutron imaging is most
commonly practiced within the aero-
space and defense industries,” the report
states, “other markets are incorporating
it into their processes to improve quality,
safety, and accuracy in a variety of appli-
cations.” The report may be downloaded
at https://go.phoenixneutronimaging.
com/industry-report.
PHOENIXNEUTRONIMAGING.COM
NEWMEDIA
|
SCANNER
NDE OUTLOOK FROM P. 14
J U L Y 2 0 2 4 • M A T E R I A L S E V A L U A T I O N 15